Quick Closing Values -Remotely Operated

- With reference to remotely operated quick closing valves:
(a) state their purpose;(2)
(b) state where they would be fitted;(3)
(c) describe how they are tested.(5)

With reference to tank quick closing valves:
(a) describe, with the aid of sketches, TWO methods for remote actuation;(6)
(b) state where they would be fitted;(2)
(c) explain why they are fitted.(2)
2. Quiz. Study Notes.

With reference to quick closing valves:
(a) state where they would be fitted;(2)
(b) explain how they operate should a fire occur in EACH of the following:
the machinery space;(4)
(ii) close proximity to the valve.(4)
3. Quiz. Study Notes.

(a) State the purpose of fitting isolating valves in a ring fire main.(2)
(b) State the type of valve that should be fitted for isolating sections of a ring fire main.(2)
(c) Explain why the type of valve stated in part (b) is used.(3)
(d) State how it is ensured that the isolating valve will operate when required.(1)
(e) State the position of the machinery space isolating valve.(2)

(a) State, with reasons, the type of valve that should be used in EACH of the following situations:
(i) isolating valve within a fire main;(2)
(ii) main engine stand-by cooling water circulating pump discharge.
(2)
(b) With reference to a fuel service tank outlet valve:
(i) describe its operation;(4)
(ii) state the reason for the operation in part (b)(i).(2)
2. Quiz. Study Notes

Sketch a cross-section through a valve suitable for use as an isolating valve in a fire main, labelling ALL parts and stating a suitable material for EACH part.(10)
3. Quiz. Study Notes

(a) State, with reasons, the type of valve that should be fitted to EACH of the following:
(i) main engine lubricating oil pump delivery;(2)
(ii) fuel service tank outlet;(2)
(iii) Ballast tank.(2)
(b) State the information required to correctly order a replacement valve.(4)

2. Quiz. Study Notes
State, with reasons, a suitable application for EACH of the following types of valve:
(a) butterfly;(2)
(b) diaphragm;(2)
(c) screw-down, non-return;(2)
(d) 3-way;(2)
(e) quick closing, screw lift.(2)

3. Quiz. Study Notes
With reference to ship’s side valves:
(a) state why grey cast iron is not a suitable material;(3)
(b) state, with reasons, TWO suitable materials;(2)
(c) state the regular maintenance that the valves should receive, outlining reasons for this maintenance.(5)

(a) Sketch a section through a bilge injection (emergency bilge) valve.(8)
(b) Describe how the valve sketched in part (a) is tested.(2)
4. Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a cross-section of a relief valve suitable for use with a fuel supply pump(6)
(b) Describe the operation of the valve sketched in part (a) (4)
5. Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a globe type screw lift valve suitable for sea water service.(7)
(b) State, with reasons, the materials used for the valve sketched in part (a).(3)
6. Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a flexible diaphragm valve. (6)
(b) Describe how the diaphragm is replaced, stating the precautions that should be taken. (4)
7. Quiz. Study Notes
(a) Sketch a section through a 3-way mixer valve.(8)
(b) State an application for this type of valve.(2)
8. Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to centrifugal pumps:
(a) explain why it is common practice to start with the discharge valve closed or throttled;(4)
(b) explain why the delivery valve must not be left closed after starting;(3)
(c) state why it is not always necessary to fit a relief valve.(3)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

A centrifugal bilge pump has not been operating satisfactorily, the air pump was tested and found to be operating correctly.
List FIVE faults that could have caused the problem, stating why EACH fault causes poor operation.(10)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to centrifugal pumps used for bilge/ballast purposes:
(a) explain the specific problems which may arise using the pumps for these purposes;(4)
(b) explain TWO methods used to improve pump performance when used for these purposes.(6)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a centrifugal pump/motor set:
(a) state FIVE indications that a fault has occurred;(5)
(b) state a possible cause of EACH fault stated in part (a).(5)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Describe, with the aid of sketches, the operating principles of a centrifugal pump.(7)
(b) State why centrifugal pumps are not self-priming.(3)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of sketch, a system for priming a centrifugal pump using a priming pump driven from the centrifugal pump
6.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to positive displacement pumps:
(a) describe, with the aid of a sketch, the operation of a pulsation damper;(6)
(b) explain why some positive displacement pump types do not require pulsation dampers.(4)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to positive displacement pumps:
(a) explain the need for a relief valve, stating where it would be fitted;(5)
(b) explain when a pulsation damper may be fitted to the delivery line, stating how it works.(5)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of a sketch, the operation of a double acting, piston type positive displacement pump.
(10)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a vane type pump, labelling ALL components. (6)
(b) Explain the operation of the pump sketched in part (a). (4)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of a sketch, the operation of a gear pump.
(10)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) State FOUR types of pumps suitable for use in a hydraulic system.(4)
(b) Explain why the pumps stated in part (a) are suitable for hydraulic systems.(6)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Explain how cavitation damage occurs within a pump.
(6)
(b) State, with reasons, TWO operational causes of increased cavitation within a pump.(4)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to compressed air systems used for starting air and control purposes:
(a) state the pressure used for starting air;(1)
(b) explain why the pressure stated in part (a) is necessary;(3)
(c) state the pressure used for control air;(1)
(d) explain why the pressure stated in part (c) is different to that stated in part (a);(3)
(e) explain why the pressure stated in part (c) is greater than that necessary to operate the control equipment.(2)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to reciprocating air compressors:
(a) state the meaning of the term bump clearance;(2)
(b) explain the effects on operation if the bump clearance is:
(i) too large;(2)
(ii) too small.(2)
(c) explain why the air temperature must be limited in the HP stage, stating how this is achieved;(2)
(d) explain how an aftercooler helps remove moisture from the air.(2)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a fully automatic, water cooled starting air compressor:
(a) state the alarms that should be fitted;(4)
(b) explain how damage from overpressure is prevented in EACH of the following:
(i) intercoolers;(3)
(ii) water jackets.(3)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Explain the circumstances under which EACH of the following devices fitted to an air compressor may operate;
(1) fusible plug;(4)
(ii) bursting disc.(4)
(b) State where EACH device in part (a) may be fitted.(2)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to compressed air systems, explain the purpose of EACH of the following:
(a) fusible plug on compressor discharge;(4)
(b) fusible plug on air receiver;(3)
(c) bursting disc on water cooled air compressor.(3)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

Explain why EACH of the following may have fusible plugs fitted.
(a) air compressor,(5)
(b) air receiver.(5)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a relief valve suitable for use on the air side of a compressor.(7)
(b) Explain how the valve sketched in part (a) is reset after overhaul.
(3)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to air compressors, explain EACH of the following:
(a) why an air filter is important;(4)
(b) why the compressor should not be allowed to run with a dirty air filter.(6)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to air receivers;
(a) list FOUR fittings on an air receiver;(4)
(b) describe the operation of TWO safety devices.(6)
9.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to main air receivers:
(a) list FOUR safety features, stating the purpose of EACH:(8)
(b) state the pressure at which the relief valve should lift.(2)
10.Quiz. Study Notes

Sketch a system that is capable of supplying compressed air suitable for use in pneumatic control equipment.(10)
11.Quiz. Study Notes
Explain the hazards of unauthorised repairs to compressed air lines.
(10)
12.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) State THREE requirements for compressed air to be utilised for control instrumentation.(3)(b) Using the Worksheet Q3, identify ALL the components shown for a system suitable for the production of compressed air for control instrumentation.(7)
13.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a starting air reservoir, labelling ALL mountings.(8)
(b) State TWO coatings that can be used to protect the interior surface of a large air reservoir against corrosion.(2)
14.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to air compressors and pneumatic control systems:
(a) state ONE advantage and ONE disadvantage of a compressed air system compared to a hydraulic system;(2)
(b) explain why it is desirable to remove moisture from the air;(2)
(c) explain why its desirable to limit oil carry over;(2)
d) describe how EACH of the following is achieved:
(i) removal of moisture from the air;(2)
(ii) limiting of oil carry over.(2)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to using air as a pneumatic medium:
(a) state FOUR advantages;(4)
(b) state, with reasons, THREE disadvantages.(6)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to accumulators in pneumatic control systems:
(a) state the TWO main purposes;(2)
(b) explain why EACH of the purposes stated in part (a) are required.(8)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to pneumatic control systems, explain EACH of the following:
(a) why moisture is undesirable;(4)
(b) why oil is generally undesirable;(3)
(c) why oil may be intentionally introduced into parts of the system.(3)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to an air supply for pneumatic control systems:
(a) state THREE contaminants that may be present;(3)
(b) explain why the contaminants stated in part (a) are undesirable.(7)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to pneumatic control systems, explain EACH of the following:
(a) why having a supply of clean dry air is important;(5)
(b) how a supply of clean dry air is achieved.(5)
6.Quiz. Study Notes
Describe TWO methods of drying compressed air for use in a pneumatic control system.(10)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of a sketch, a pressure reducing valve suitable for supplying control air from the main starting air supply.(10)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to control systems:
(a) state FIVE advantages of using pneumatics;(5)
(b) state FIVE advantages of using hydraulics.(5)
9.Quiz. Study Notes
Hydraulic Control Systems

With reference to hydraulic systems:
(a) state FOUR applications for a hydraulic system on board a vessel;(4)
(b) state the effects and possible causes of EACH of the following:
(i) air in the system;(2)
(ii) dirt and foreign particles in the system;(2)
(iii) separated water in the system.(2)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to hydraulic systems:
(a) state TWO functions of an accumulator;(2)
(b) describe, with the aid of a sketch, a gas charged diaphragm or bladder accumulator;(6)
(c) describe how the bladder is prevented from being extruded from the accumulator described in part (b).(2)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to hydraulic systems:
(a) state THREE possible contaminations;(3)
(b) state possible causes of the contaminations stated in part (a).(3)
(c) explain how the contaminants stated in part (a) are prevented from affecting the system.(4)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to water contamination of hydraulic systems:
(a) state possible sources of water:(2)
(b) explain the possible consequences; (5)
(c) describe the actions to be taken should it be suspected.(3)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

Outline the safety precautions which should be taken when carrying out repairs or maintenance on hydraulic systems.(10)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to the cleanliness of hydraulic systems on board an ocean going vessel:
(a) list FOUR contaminants;(4)
(b) describe the steps that should be taken to eliminate the contaminants listed in part(a).(6)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a windlass that is hydraulically operated by a variable displacement motor, explain the effect of changing EACH of the following:
(a) the flow rate of hydraulic oil;(4)
(b) the displacement of the motor.(6)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of sketches, TWO methods for controlling the speed of a hydraulic motor.(10)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to two ram steering gears which incorporate spherical bearings:
(a) sketch an arrangement of rams and tiller, including fittings;(6)
(b) explain why spherical bearings are required on the ram ends.(4)
Question 5. Most, not all, make a reasonable sketch but few can then relate the sketch, or use it, to show the need for spherical bearings.
Sketch a 2-ram type steering gear including the hydraulic circuit, labelling ALL components.(10)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a hydraulic steering gear, describe TWO methods that may be used to prevent the idle pump from motoring.(10)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a hydraulic steering gear:
(a) state the purpose of the hunting gear;(2)
(b) explain, with the aid of sketches, the action of the hunting gear.(8)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to steering gears, explain the meaning of EACH of the following
(a) 100% redundancy:(5)
(b) single failure criteria.(5)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to an electro-hydraulic steering gear, explain EACH of the following:
(a) how steering may be maintained should the telemotor system fail;(5)
(b) how steering may be achieved should there be total failure of the hydraulic system.(5)
Question 5. Few mention procedures. Many continue to use the steering gear hydraulically using manual pump etc, even though the question says that there is complete hydraulic system failure.
6.Quiz. Study Notes
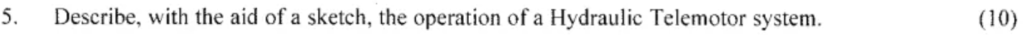
Describe, with the aid of a sketch, the operation of a Hydraulic Telemotor system.(10)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) State the rudder movement required by SOLAS II-I, Reg 29.(5)
(b) Explain how it is ensured that the maximum movement stated in part (a) is not exceeded in an electro-hydraulic, ram type steering gear.(2)
(c) Explain how the steering gear system is protected from damage should the maximum movement be exceeded.(3)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

Sketch a valve operated, rotary vane steering gear, showing the hydraulic system from the directional valve to the rotary vane unit.
(10)
9.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of a block diagram, the operation of an automatic steering system, including auto-pilot and valve operated steering gear.
(10)
Question 5.
Very poor. Many do not understand the term ‘block diagram’, many simply sketch and describe a steering gear. Of those that try to describe the basics of control, they appear to believe that the rudder angle is fed back to the auto-pilot-i.e that the rudder has a set angle required to maintain the vessel on course rather than the rudder moving from centre to return the vessel to the set course. Rudder feedback is used to limit the rate of change of course but none mention this. Several make no attempt.
10.Quiz. Study Notes
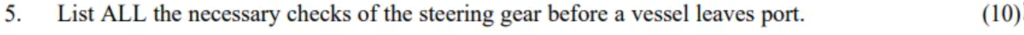
List ALL the necessary checks of the steering gear before a vessel leaves port.(10)
Question 5. Candidates lose marks by not mentioning alarms, emergency power supply and not actually inspecting the gear.
11.Quiz. Study Notes

Using the Worksheet Q5, sketch the hydraulic system for the two ram steering gear shown. The system should be capable of ensuring that steerage may be maintained should hydraulic pipe failure occur at any point.(10)
12.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to controllable pitch propellers:
(a) describe a mechanism that changes the pitch of the blades;(7)
(b) explain how the pitch of the blades is indicated.(3)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to controllable pitch propellers:
(a) explain why they should maintain a small amount of pitch when in the neutral position;(3)
(b) state, with reasons, the failsafe position;(4)
(c) explain how pitch may be restored should hydraulic system failure occur.(3)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a vessel with a single electro/hydraulic controllable pitch propeller, explain EACH of the following:
(a) how manoeuvring may be maintained if the control system fails;(5)
(b) the action to be taken should the hydraulic system irreparably fail whilst on route and the blades assume zero pitch.(5)
Question 6.
Some do not understand the term Electro-Hydraulic. Some use engines to manoeuvre even though the question states a single CPP. There is more to maintaining manoeuvring than just switching to the local control. The question states that the CPP assumes zero pitch on failure of the hydraulics – this is therefore the fail safe position. Several appear to have a further spring in the hub to give pitch on the blade.
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to controllable pitch propellers:
(a) describe a mechanism that changes the pitch of the blades; (7)
(b) explain how the pitch of the blades is indicated.(3)
Question 6. Several answer this question by describing the whole system, the question just asks about the mechanism for changing the blade angle. Of those that describe the mechanism, most mention longitudinal movement and angular but none actually explain how longitudinal is changed to angular. Several make no attempt
4.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to propellers, explain EACH of the following:
(a) TWO advantages of having high skew;(5)
(b) TWO advantages of aft rake.(5)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) State SIX advantages of controllable pitch propellers.(6)
(b) State FOUR disadvantages of controllable pitch propellers.(4)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to propellers, explain EACH of the following terms:
(a) skew;(2)
(b) rake;(2)
(c) pitch;(2)
(d) slip.(4)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch an arrangement for a transverse, water jet thruster.(6)
(b) Explain how thrust is created in a water jet thruster.(4)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe the advantages of using water jets instead of conventional propellers for vessel propulsion.(10)
Question 6. Many simply state advantages the question says ‘describe”. Many of the advantages claimed could be equally applied to CPP’s and D/E drives, both of which are now considered conventional.
9.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of a sketch, the operation of a transverse thruster that is hydraulically driven.(10)
Question 6. Generally poor answers. Several just describe the hydraulic control, describing operation must include how thrust is varied in magnitude and direction as well as control.
10.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Describe, with the aid of a sketch, a pilgrim nut.(5)
(b) Explain how the pilgrim nut is used to ensure correct fitting of a keyless propeller.(5)
11.Quiz. Study Notes
Main Propulsion Shaft

With reference to main propulsion shaft hydraulic sleeve type couplings:
(a) describe, with the aid of a sketch, the removal procedure;(7)
(b) state how it is determined, during reassembly, that the push fit is complete.(3)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to main propulsion shaft hydraulic sleeve type couplings:
(a) describe, with the aid of a sketch, the tightening procedure;(7)
(b) state how it is determined that the push fit is complete.(3)
Question 7.
Some sketches are very poor and show little understanding of the mode of operation of the coupling, this is then reflected in the answer. Many think that the separation oil is only for lubrication.
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to comparing modern water lubricated stern tube bearings with those that are oil lubricated:
(a) state THREE advantages; (3)
(b) state THREE disadvantages, explaining how EACH may be overcome.(7)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

Whilst a single screw vessel is on passage it is noticed that an intermediate shaft bearing is running hot.
(a) State FIVE possible causes.(5)
(b) Explain the procedure that should be followed in order to reach port for further investigation if there were no further causes.(5)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to propulsion shaft intermediate bearings of the plain bearing type, explain EACH of the following:
(a) how change of alignment due to vessel condition is allowed for;(2)
(b) why the shaft must be able to move longitudinally;(4)
(c) why the aftmost bearing requires a complete bush but other bearings may have the bush only in the lower half.(4)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to stern bearings, state the advantages and disadvantages of using EACH of the following:
(a) white metal;(5)
(b) plastic.(5)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a flexible coupling that could be used for a main propulsion drive.(7)
(b) State THREE reasons for using a flexible coupling in propulsion drives.(3)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to propulsion shaft intermediate bearings of the plain bearing type, explain EACH of the following:
(a) how change of alignment due to vessel condition is allowed for(2)
(b) why the shaft must be able to move longitudinally (4)
(c) why the aftnost bearing requires a complete bush but other bearings may have the bush only in the lower halt.(4)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to intermediate shaft bearings of the roller type, describe, with the aid of a sketch, EACH of the following:
(a) how some angular misalignment of the shaft is accommodated;(5)
(b) how longitudinal movement of the shaft is accommodated.(5)
Question 7.
The question is all about roller type intermediate bearings. Many candidates describe thrust block and shaft alignment methods.
9.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe the inspection of a main thrust bearing.(10)
10.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe, with the aid of sketches, the fitting of a hydraulically tensioned bolt suitable for main propulsion shaft flanges.(10)
11.Quiz. Study Notes

Sketch an arrangement for the aft seal of an oil lubricated stern tube bearing.(10)
12.Quiz. Study Notes
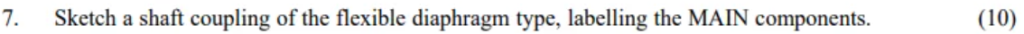
Sketch a shaft coupling of the flexible diaphragm type, labelling the MAIN components.(10)
13.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Describe. with the aid of a sketch, how the alignment of a propeller transmission shaft system may be checked. (8)
(b) State the indications of a high bearing when the shaft is running.(2)
Question 7. Many attempt to describe aligning two shafts together rather than checking the alignment of the shafting. Candidates describe measuring along the shaft rather than the height of the bearings.
14.Quiz. Study Notes

Explain THREE advantages of hydraulically fitted shaft coupling bolts compared to parallel, interference fit bolts.
15.Quiz. Study Notes
Trips, Alarms, Fuses

Explain EACH of the following electrical terms:
(a) preferential tripping;(2)
(b) sequential starting;(2)
(c) fuse back up protection;(2)
(d) discrimination;(2)
(e) non-essential consumer.(2)
Question 8.
Candidates struggle with sequential starting, the reason for back up fuses and discrimination. Most state circuits for propulsion are the only essential circuits.
1.Quiz. Study Notes

Explain how EACH of the following electrical safety devices may be tested for correct operation:
(a) a generator reverse power trip;(2)
(b) generator over-current alarm;(2)
(c) generator over-current trip;(2)
(d) emergency generator auto start up;(2)
(e) preferential tripping sequence(2)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

Explain, with the aid of sketches, how a new motor is aligned with an existing pump.(7)
State THREE checks which should be made before using the pump after the motor has been aligned.(3)
Question 8.
Many do not explain how the alignment is checked – simply stating use dial indicator with a sketch of it in position is not enough. Some, not many, mention shims but none actually explain which shims would be adjusted to change the alignment or that angular misalignment can be in more than one plane.
3.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Explain how propeller thrust is transmitted to a vessel’s hull.(3)
(b) Describe the mounting arrangements of a thrust block to the hull.(4)
(c) Explain why the clearance between the thrust block pads and collar is critical.(3)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Describe the operation of a preferential trip.(5)
(b) State the type of circuits that cannot be connected to the preferential trip, listing THREE examples.(5)
5.Quiz. Study Notes
Earth Faults

(a) State FIVE causes of earth faults.(5)
(b) Explain how EACH fault stated in part (a) could be rectified.(5)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Compare the effects of earth leakage occurring in an earthed distribution system and in an insulated distribution system.(6)
(b) State the reasons why an instrument type earth leakage detector will be fitted in preference to simple earth lamps.(4)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to electrical maintenance:
(a) explain the procedure for proving a motor circuit is dead using a multimeter;(5)
(b) explain the procedure for testing the insulation resistance and earth bonding of the motor, giving examples of acceptable readings.(5)
3.Quiz. Study Notes
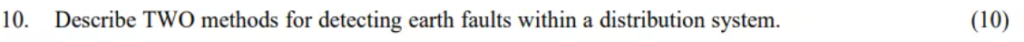
Describe TWO methods for detecting earth faults within a distribution system. (10)
4.Quiz. Study Notes
Switchboard

(a) State FIVE devices fitted to a main distribution switchboard in order to protect a.c. generators that can be operated in single or parallel mode.
(5)
(b) Explain why EACH device stated is needed.(5)
Question 9.
The question asks about devices for protection of generators, many include pref trip and other devices that are for protection of distribution. Most, when answering about the reason for a device, simply state what it does-i.e over-current protection protects against overcurrent. The question is asking for the reason for the device-i.e what would overcurrent do to the generator.
1.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Describe, with the aid of a sketch, a cartridge type fuse.(7)
(b) State why a fuse used in a motor circuit differs from a fuse used in a lighting circuit.(3)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a line diagram of an emergency switchboard arrangement, labelling the MAIN components.(6)
(b) Explain how main electrical power is restored to the emergency switchboard after a blackout, stating the precautions necessary. (4)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to shore supplies:
(a) state THREE necessary parameters that must be checked before connecting to the vessel’s distribution system;(3)
(b) explain the possible consequences of connecting an incorrect shore supply.(7)
Question 9.
Several mention the parameters and then totally ignore them in part b. Many state what will occur but not the consequences eg high current but not explaining that this will cause overheating and damage.
4.Quiz. Study Notes

5.Quiz. Study Notes
With reference to the connection of shore power supply on a vessel that does not have a shore power converter:
(a) list the items that would be included on a checklist for supply of power to the vessel;(7)
(b) state the effects of running a 60Hz vessel on a 50Hz supply.(3)
AC Generators

(a) State THREE devices fitted to the main breakers to protect a.c. generators that are able to run in parallel.(3)
(b) Explain why EACH device stated in part (a) is fitted.(7)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) State the factor that determines the minimum number of available generators required for a vessel to put to sea.(3)
(b) State SEVEN essential services for the operation of a vessel.(7)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to a.c. generators:
(a) explain why they must be synchronised before connecting in parallel;(6)
(b) list TWO devices for ensuring that synchronising is correct;(2)
(c) state how the devices listed in part (b) indicated that synchronising is correct.(2)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe the routine maintenance that should be carried out on the electrical side of an a.c. generator set.
(10)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe the FULL procedure for paralleling an incoming a.c generator to another a.c generator connected to the main switchboard.(10)
5.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Explain the term single phasing.(2)
(b) State the effects on a motor of single phasing.(6)
(c) State how single phasing may be protected against in the motor starter circuit.(2)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

Describe the construction of a three phase induction motor of the caged rotor type.(10)
7.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Describe the construction of a salient pole a.c. generator rotor.(6)
(b) Explain how many poles would be required for a 50Hz supply, rotational speed of 750rpm.(4)
8.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) Sketch a block diagram of the layout of a vessel electrical distribution system, including the main and emergency generators and detailing the main consumers supplied by the emergency board.(7)
(b) Describe the MCA recommended procedure for testing the Emergency Alternator.(3)
9.Quiz. Study Notes
Storage Batteries

With reference to storage batteries, explain EACH of the following:
(a) boost charge;(3)
(b) slow charge;(2)
(c) trickle charge;(3)
(d) float charge.(2)
1.Quiz. Study Notes

(a) List FIVE safety precautions that need to be observed for the location and storage of a large bank of emergency batteries.(5)
(b) Describe FIVE weekly routine maintenance tasks that need to be performed on a bank of lead acid battery cells.(5)
2.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to battery lockers:
(a) state the requirements for an internal light fitting;(4)
(b) explain why the requirements stated in part (a) are necessary.(6)
3.Quiz. Study Notes

With reference to storage batteries:
(a) explain how the level of charge can be determined in EACH of the following:
(i) lead acid;(3)
(ii) alkaline;(2)
(b) state FIVE reasons that the charge may be reduced.(5)
4.Quiz. Study Notes

List FIVE safety devices that may be fitted to the main swichboard of a vessel, stating reasons for fitting each device.(10)
5.Quiz. Study Notes
State FIVE safety features of a battery locker, explaining why EACH feature is required.(10)
6.Quiz. Study Notes

List TEN routine maintenance checks that should be carried out on a vented type lead acid engine starting battery system.(10)
Question 9.
Mostly well answered
7.Quiz. Study Notes
To be sorted (Misc)
