
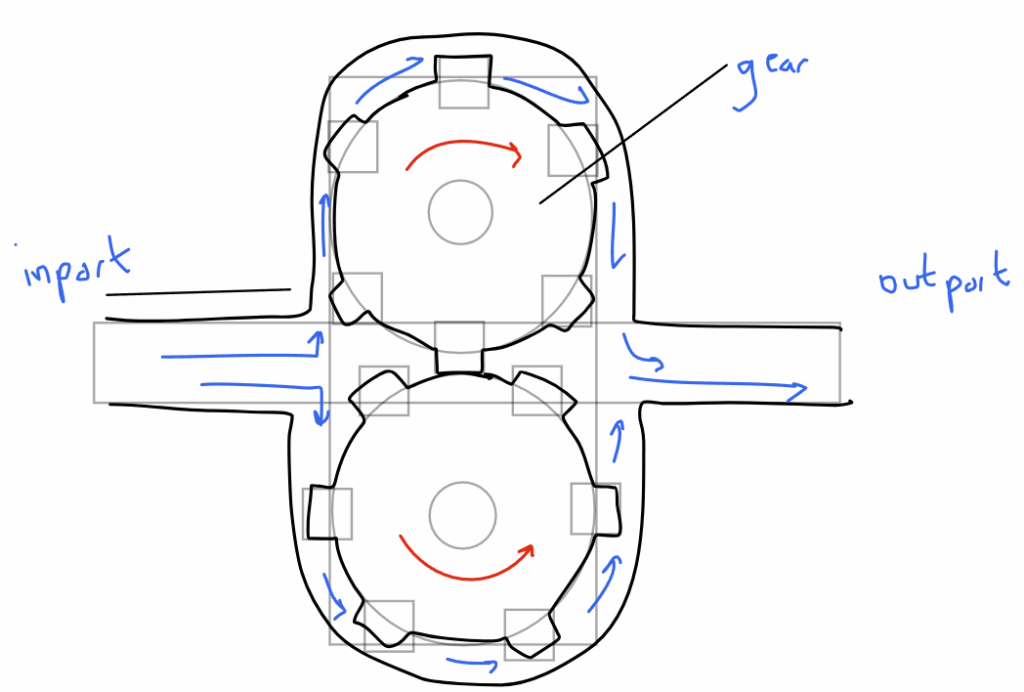
A gear pump utilizes meshing gears to transfer fluids in a positive displacement manner. Here’s a breakdown of its operation:
Components:
- Housing: The main body of the pump that encloses all the internal components.
- Gears: Two interlocking gears, typically spur gears with identical profiles.
- Inlet Port: The opening where the fluid enters the pump chamber.
- Outlet Port: The opening where the pressurized fluid exits the pump.
Operation:
- Rotation: The gears rotate in opposite directions, driven by a shaft or motor.
- Suction Creation: As the gears rotate, the spaces between their teeth on the suction side increase in volume. This creates a low-pressure zone at the inlet port, drawing fluid into the pump chamber.
- Trapping Fluid: The meshing of the gears at the center of the pump traps the fluid within the spaces between their teeth.
- Displacement and Pressure Build-Up: Continued rotation forces the trapped fluid around the outside of the gears and towards the discharge port. The decreasing volume between the meshing teeth and the housing progressively increases the pressure of the trapped fluid.
- Discharge: The high-pressure fluid is expelled from the pump through the discharge port.
Key Points:
- Positive Displacement: The fixed volume between the gears ensures a constant amount of fluid is delivered with each rotation, regardless of the discharge pressure.
- Low Pressure Drop: The design allows for smooth fluid flow within the pump chamber, minimizing internal pressure losses.
- High Viscosity Fluids: Gear pumps are well-suited for pumping viscous fluids due to their positive displacement nature and relatively low shear forces applied to the fluid.
- Tight Clearances: The clearances between the gears and the housing are minimal to ensure efficient pumping and prevent internal leakage.
Additional Notes:
- Depending on the design, some gear pumps may have crescent-shaped seals between the gears and the housing to further improve sealing and efficiency.
- Gear pumps can be bi-directional, meaning they can pump fluid in either direction depending on the direction of rotation of the gears.