

Starting Air Reservoir and Corrosion Protection
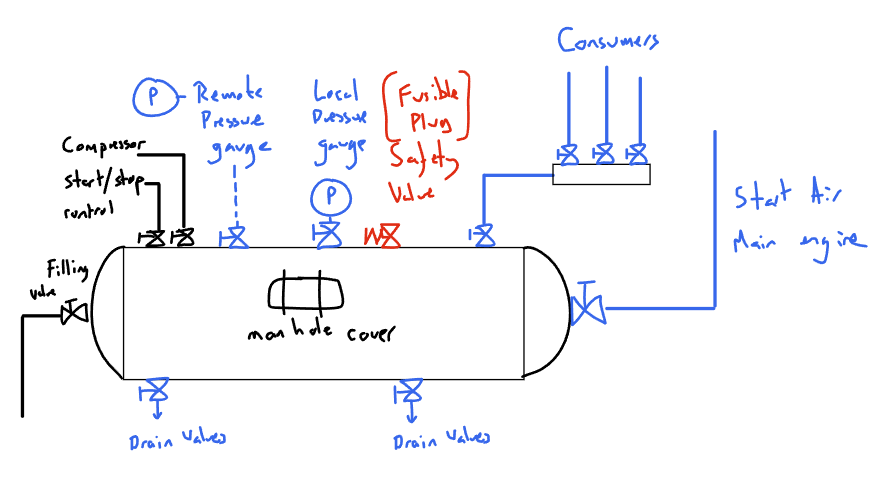
(a) Starting Air Reservoir Mountings:
A starting air reservoir is a pressure vessel used to store compressed air for engine starting purposes. Here’s a description of the typical mountings used for a starting air reservoir:
- Saddle Supports: These are the most common type of mounting. The reservoir rests on two or more cradles (saddles) welded or bolted to a solid foundation. The saddles distribute the weight of the reservoir evenly and provide stability.
- Trunnion Mounts: For larger or horizontal reservoirs, trunnion mounts might be used. Trunnions are cylindrical shafts welded to the ends of the reservoir that fit into bearing blocks on the support structure. This allows the reservoir to pivot slightly, accommodating thermal expansion and contraction.
- Bracket Mounts: In some cases, particularly for smaller reservoirs, brackets welded or bolted to the reservoir shell can be used to secure it directly to a wall or support structure.
Additional Considerations:
- Anchor Bolts: Regardless of the mounting type, the reservoir will likely be secured to the foundation using anchor bolts to prevent excessive movement or tipping due to forces exerted during pressurization or engine starting.
- Vibration Isolation: In some applications, vibration isolation pads or mounts might be placed between the reservoir and its supports to dampen vibrations transmitted to the surrounding structure.
(b) Coatings for Interior Corrosion Protection:
The interior surface of a large air reservoir is susceptible to corrosion due to moisture present in the compressed air. Here are two common coatings used for protection:
- Zinc Rich Epoxy:
- Composition: This coating consists of a zinc-rich primer with an epoxy resin topcoat. The zinc particles in the primer act as sacrificial anodes, corroding preferentially to protect the steel substrate. The epoxy topcoat provides additional protection against moisture and chemical attack.
- Benefits: Zinc rich epoxy offers good adhesion, flexibility, and cathodic protection. It’s a widely used and cost-effective solution for protecting air receiver interiors.
- Polyurethane:
- Properties: Polyurethane coatings are known for their excellent chemical resistance, abrasion resistance, and flexibility. They form a tough, impermeable barrier against moisture and corrosive elements.
- Applications: Polyurethane coatings are a good choice for air receivers operating in harsh environments or where there might be exposure to contaminants in the compressed air.
Additional Considerations:
- Surface Preparation: The success of any coating system relies heavily on proper surface preparation. The interior surface of the air receiver needs to be thoroughly cleaned and blasted to remove rust, mill scale, and other contaminants before coating application.
- Coating Selection: The choice of the most suitable coating depends on factors like operating pressure, temperature, budget, and potential exposure to contaminants within the compressed air system. Consulting with a qualified coatings specialist is recommended for selecting the optimal coating solution.