Study Notes Quiz

With reference to Discontinuous or On Off control systems:
(a) sketch the response of a basic heater control, showing temperature against time and labelling the key points;(4)
(b) state THREE methods of improving the accuracy/speed of response(6)
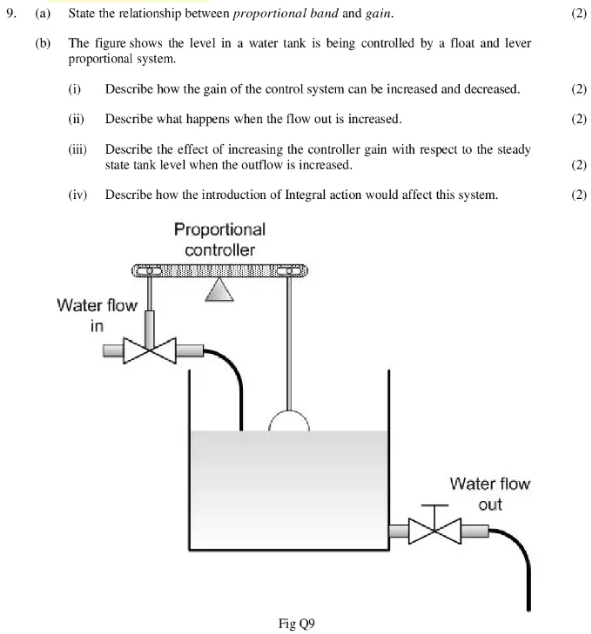
(a) State the relationship between proportional band and gain.
(b) The figure shows the level in a water tank is being controlled by a float and lever proportional system.
(i) Describe how the gain of the control system can be increased and decreased.
(ii) Describe what happens when the flow out is increased.
(iii) Describe the effect of increasing the controller gain with respect to the steady state tank level when the outflow is increased.
(iv) Describe how the introduction of Integral action would affect this system.

(a) Explain EACH of the following control terms:
(i) proportional bandwidth;(2)
(ii) integral action;(2)
(iii) derivative action.(2)
(b) Describe a 3-step method for tuning a PID controller.(4)

(a) Define the term Proportional Action.(2)
(b) Explain the purpose of Integral Action.(2)
(c) Describe a possible effect of excessive Integral Action.(2)
(d) Explain the purpose of Derivitive Action.(2)
(e) Describe the effect of excessive Derivitive Action.(2)

With reference to hydraulic governors fitted to alternators designed to run in parallel:
(a) explain why these governors have adjustable integral action;(5)
(b) explain, with the aid of a load/frequency diagram, how two generators operating in parallel are able to achieve a stable load share with a 50/50 ratio.(5)

(a) Describe, with the aid of a control block diagram, how a governor maintains the speed of a diesel engine driving a generator.(6)
(b) Describe the reasons for Integrating the error signal and the effect it has on the governor fuel rack.(4)

(a) State the reasons for fitting a pneumatic process valve with EACH of the following:
(i) a volume booster;(2)
(ii) a feedback positioner.(2)
(b) State, with reasons, the type of actuator fitted to the process valves for EACH of the following systems:
(i) a fuel supply system in which the valve must not move on loss of power to the control system;(3)
(ii) a lubrication oil cooling system in which the valve diverts the oil through a cooler.(3)

With reference to engine governors, explain EACH of the following terms:
(a) sensitivity;(2)
(b) hunting;(2)
(c) speed droop;(2)
(d) stability;(2)
(e) isochronous governing.(2)

Explain EACH of the following control terms:
(a) settling time;(2)
(b) repeatability;(2)
(c) dead zone;(2)
(d) hysteresis;(2)
(e) proportional bandwidth.(2)
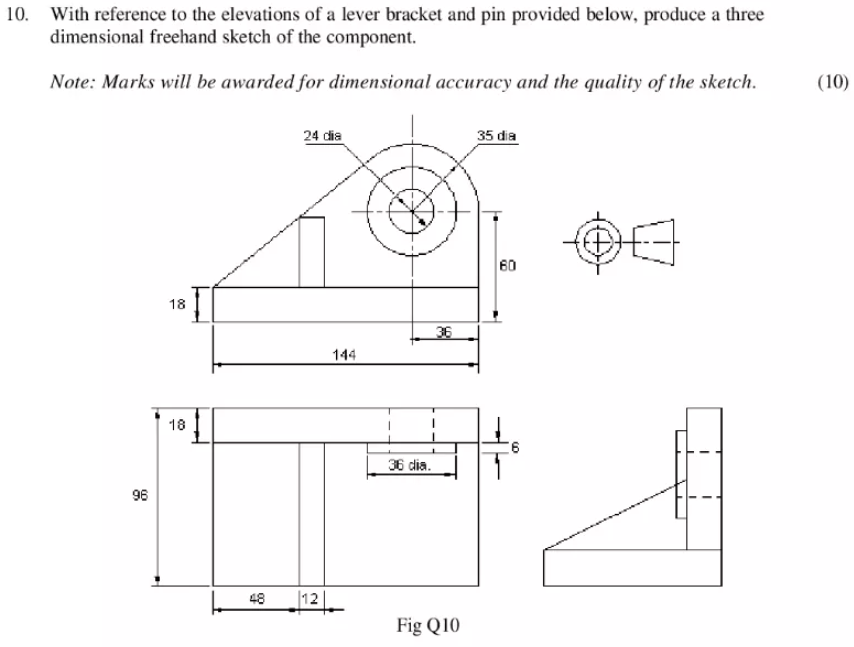
With reference to the elevations of a lever bracket and pin provided below, produce a three dimensional freehand sketch of the component.
Note: Marks will be awarded for dimensional accuracy and the quality of the sketch.