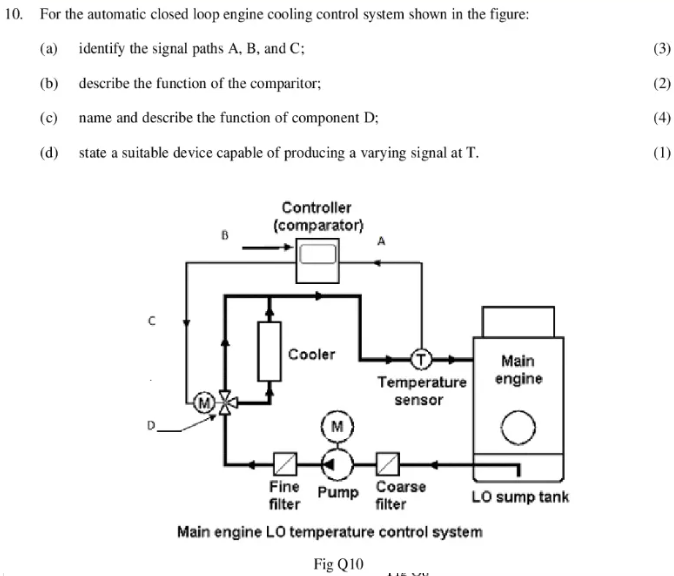
(a) Signal paths:
- Path A: This path carries the coolant temperature signal from the temperature sensor to the comparator.
- Path B: This path carries the control signal from the comparator to the cooler (fan).
- Path C: This path represents the coolant flow through the engine, cooler, and back to the engine.
(b) Comparator function:
The comparator compares the coolant temperature signal (Path A) with a reference voltage (setpoint temperature). If the coolant temperature is higher than the setpoint, the comparator outputs a high signal to Path B. This high signal activates the cooler (fan) to start cooling the engine. When the coolant temperature reaches the setpoint, the comparator outputs a low signal, turning off the cooler (fan).
(c) Component D and its function:
Component D is a fine filter. Its function is to remove fine particles from the coolant to protect the engine and other components from wear and tear.
(d) Device at T for varying signal:
A suitable device capable of producing a varying signal at T would be a temperature sensor. This sensor would convert the engine oil temperature into an electrical signal. This signal could then be used to adjust the setpoint temperature of the comparator based on the engine’s operating conditions. This would allow for more dynamic and efficient cooling control.