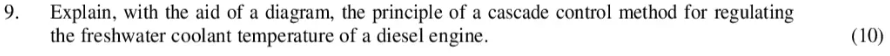
Cascade Control for Diesel Engine Coolant Temperature:
The cascade control method involves two nested control loops to regulate the freshwater coolant temperature in a diesel engine with increased stability and accuracy. Here’s the explanation with a diagram:
Components:
- Primary Loop:
- Sensor: Measures freshwater coolant temperature (T_coolant).
- Primary Controller: Compares T_coolant with the desired setpoint (T_setpoint).
- Actuator: Regulates the coolant flow rate (e.g., by adjusting a control valve).
- Secondary Loop:
- Measured Variable: Represents the manipulated variable of the primary loop (e.g., valve position or flow rate).
- Secondary Controller: Maintains the manipulated variable at the desired value set by the primary controller.
- Secondary Actuator: Directly controls the manipulated variable (e.g., adjusts the valve motor).
Diagram:
Operation:
- Primary Loop:
- The sensor measures T_coolant and sends the signal to the primary controller.
- The controller compares T_coolant with T_setpoint and calculates the error.
- The error is multiplied by the primary gain to generate a control signal.
- This signal adjusts the actuator (e.g., valve) to regulate the coolant flow rate.
- Secondary Loop:
- The secondary sensor measures the manipulated variable (e.g., valve position or flow rate).
- This value is compared with the desired value set by the primary controller.
- Any deviation triggers the secondary controller.
- The secondary controller generates a signal to adjust the secondary actuator (e.g., valve motor).
- This fine-tunes the manipulated variable to precisely match the primary controller’s demand.
Benefits of Cascade Control:
- Improved Stability: The secondary loop compensates for disturbances affecting the manipulated variable, preventing them from influencing the primary loop and coolant temperature.
- Faster Response: The secondary loop acts directly on the manipulated variable, leading to quicker adjustments and reduced settling time.
- Reduced Sensitivity: The primary controller focuses on the overall temperature control, while the secondary loop handles the actuator dynamics, making the system less sensitive to actuator characteristics.
Overall, cascade control provides a more robust and accurate solution for regulating the freshwater coolant temperature in a diesel engine, especially when dealing with external disturbances or complex actuator dynamics.